
In the electronic devices we use daily—such as remote controls, smartphones, refrigerators, TVs, air conditioners, and computers—there is a crucial component called the Printed Circuit Board (PCB). The name comes from the way its electrical circuits are formed, similar to early book printing. Some also refer to it as a Printed Wire Board (PWB).

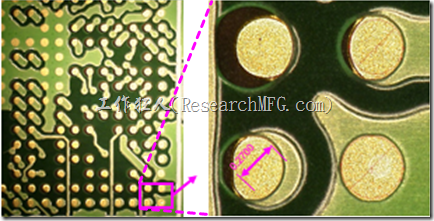 Recently, our company started a new project, and the R&D team has been pushing PCB layout requirements to the extreme. As PCBs size get smaller, the
Recently, our company started a new project, and the R&D team has been pushing PCB layout requirements to the extreme. As PCBs size get smaller, the 

