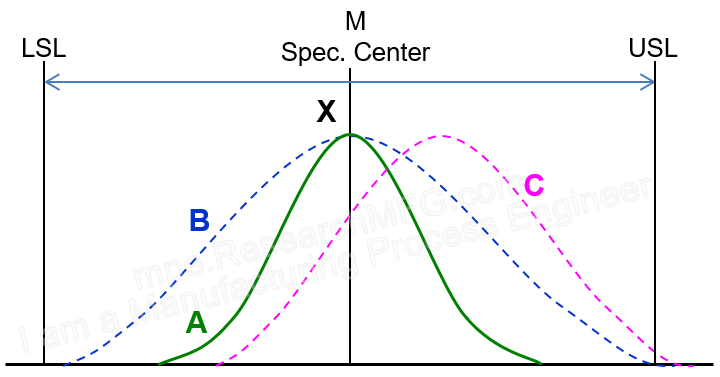
Workingbear has always wanted to write an article about “Quality Engineers,” because in most factories, quality engineers, product/process engineers, and test engineers are often called the “three major engineering departments” in manufacturing. Of course, there are also production, machine maintenance, and other departments in the factory.
However, since Workingbear has never officially worked in quality control, some of the opinions here may be biased or influenced by personal preference. Different viewpoints are welcome in the comments, but no name-calling, please.
read more…》