Process capability refers to the ability of a production process to consistently produce products that meet quality requirements under stable and fixed production conditions. To understand process capability, there are at least two key aspects we need to consider:
A manufacturing process’s capability is influenced by many factors, starting from product design, including materials, machines, equipment, methods, operator skills, inspection equipment, inspection methods, and the skill of the inspectors. Any changes in these factors can more or less affect process capability.
Therefore, before we talk about process capability, we must first fix all the variables that may influence it. This means creating and strictly following a Standard Operation Procedure (SOP), which standardizes every step in the process, including specifying the exact amounts of materials added at each stage.
Once all these factors are standardized and properly implemented—and the process is under stable control—then we can evaluate the true engineering capability of that process. Also, since process capability is often assessed through measurements, we need to quantify the steps in the process. For example, in a printing process, you can measure pressure, speed, temperature, and position, all of which can be tracked numerically and controlled.
What Can We Do After Understanding Process Capability?
By calculating process capability based on the two key conditions above, we can understand the achievable capability of a certain process under a specific set of conditions. From there, we can use this information in several ways:
-
Provide data for new product design or quality improvement of existing products.
-
Verify whether new or repaired equipment can meet acceptable process capability levels.
-
Assist in choosing different materials, hiring new operators, or adopting new methods.
-
Develop experimental plans by adjusting production factors to find the optimal process parameters.
-
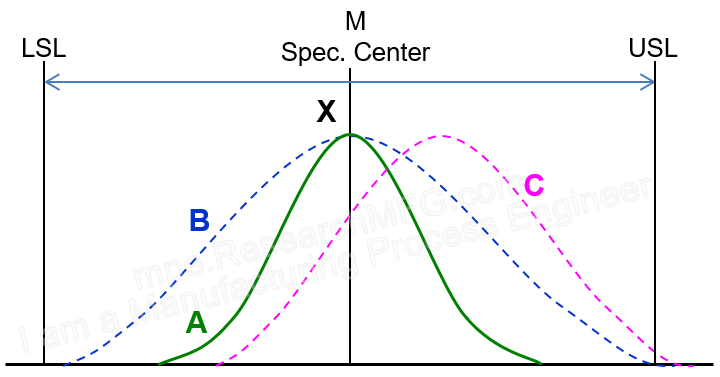
When the process capability is much better than the tolerance range, we can set an optimal target value to enable the most cost-effective production.
However, in real-world production, quality variations often occur due to changes in production factors, making it hard to maintain ideal process capability. That’s why we need to regularly monitor and evaluate the quality of each process.
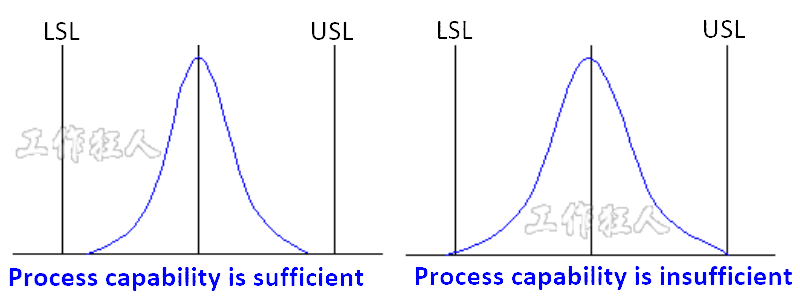
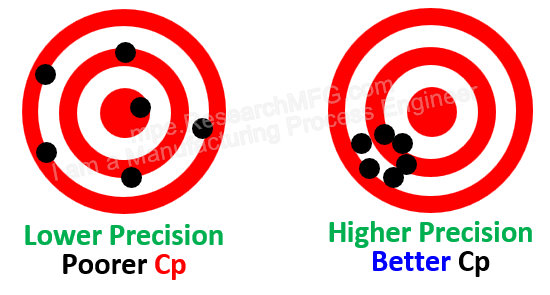
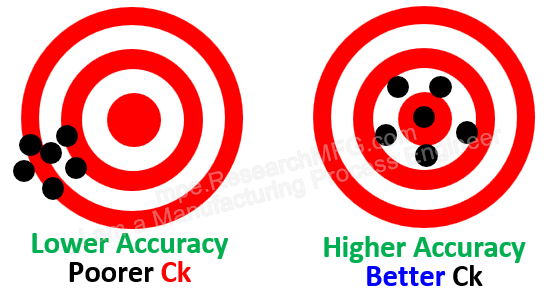
Typically, we use control charts or Cpk analysis methods to achieve this goal.
》Overview and Explanation of SPC, Cpk, and Process Capability
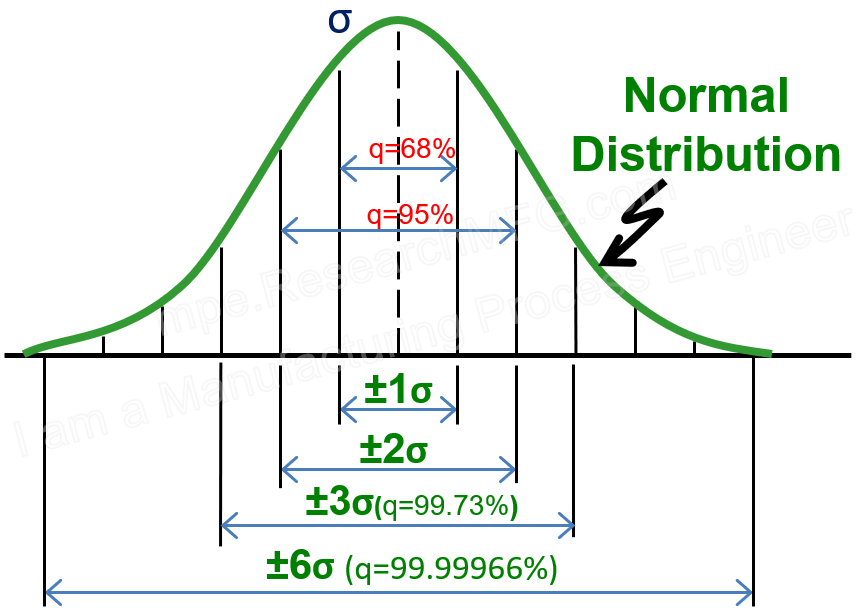
About Statistical Process Control (SPC):




Leave a Reply