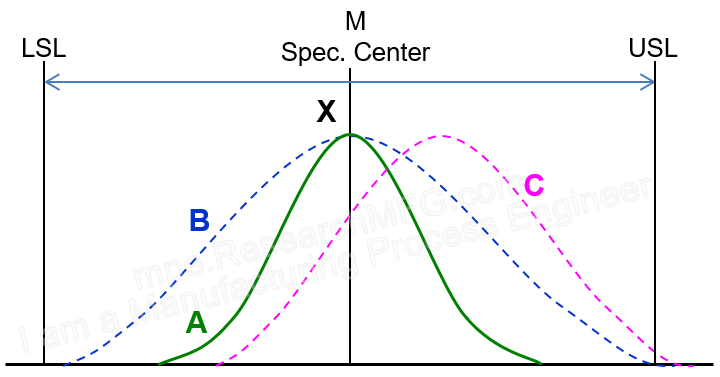
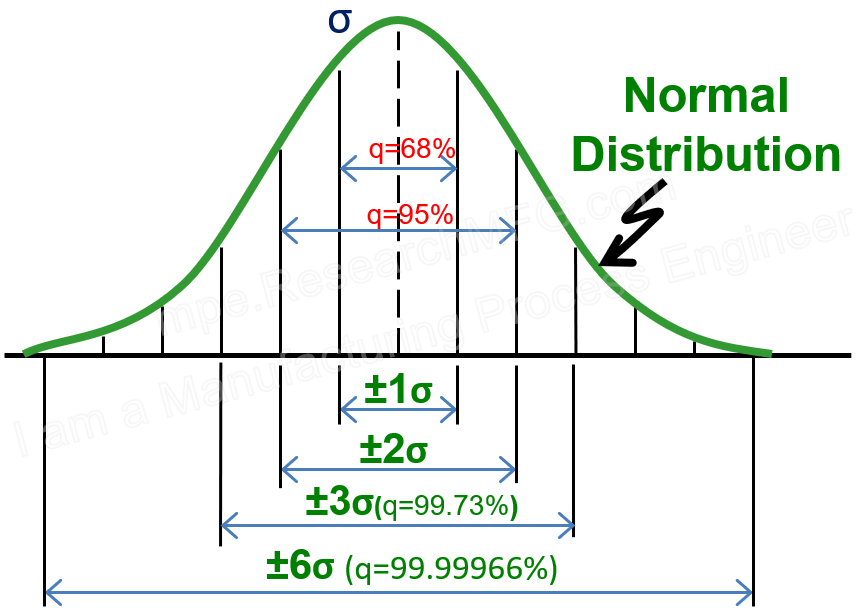
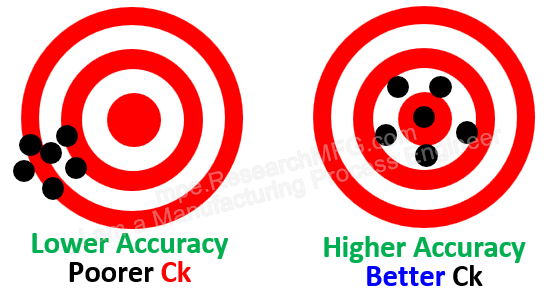
In earlier articles, we talked about three statistical indicators for process capability: Cp, Ck, and Cpk. But some people may still feel unclear about what these really mean. Let’s use normal distribution charts to explain them in a simpler way.
Visual Evaluation of Process Capability
Here’s a “normal distribution curve” that represents process capability for a typical product:
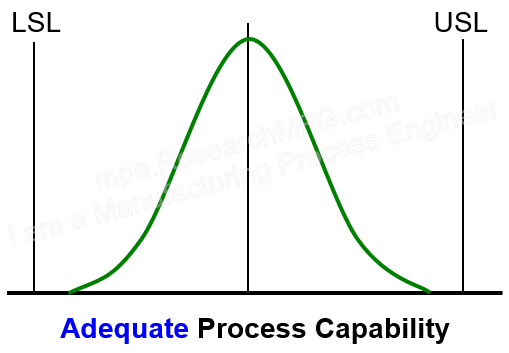
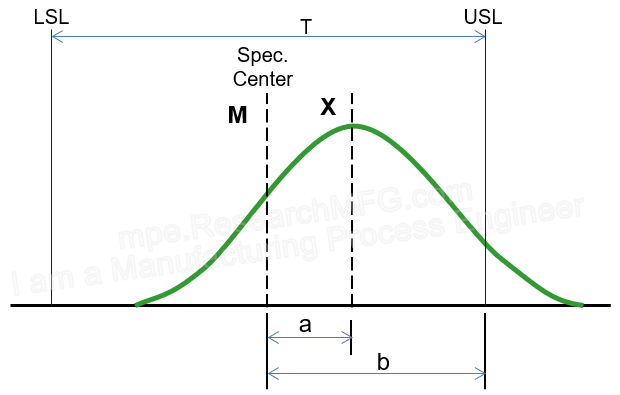
| ▼In the first chart, the middle of the process data is very close to the target (center of the spec). This means the process is well-centered, so Ck is very small — which is good. The spread of the data is about the same as the allowed spec range, which means Cp is acceptable, and the data stays within the limits with just a small margin. → This means the process capability is good enough, with a little extra allowance for small shifts in the center. |
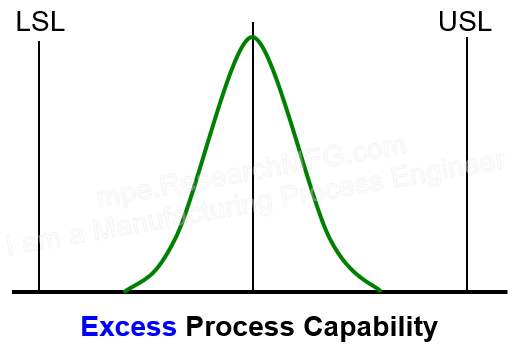
▼In the second chart, the data is also centered very well (so Ck is very small). But this time, the spread of the data is much narrower than the allowed spec range, which means Cp is very high — even better. The data is well inside the limits, leaving a lot of safety margin. → This suggests the process capability is more than enough. It might mean the machines are too good for this job, or that the specs are too loose. In this case, you could even produce higher-end products with tighter tolerances. |
|
 |
 |
| ▼The center of this process capability chart is close to the target, but the width just touches the spec limits. This means Ck is very good, but Cp is only barely acceptable. → Most products will meet the spec, but a small number may fall outside. The process needs improvement to narrow the distribution width. |
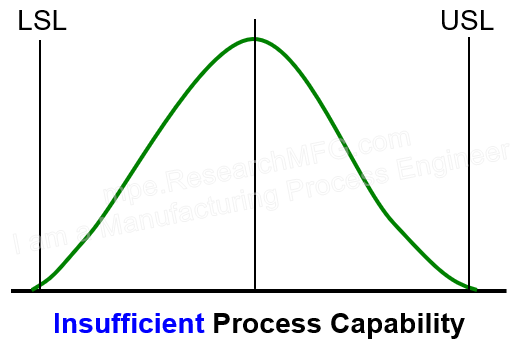
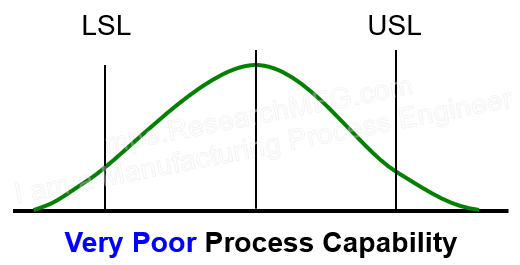
▼The center is close to the target, but the width goes a bit beyond the spec limits. This means Ck is good, but Cp fails. → This means many products will be out of spec. Immediate corrective action is needed. |
|
 |
 |
|
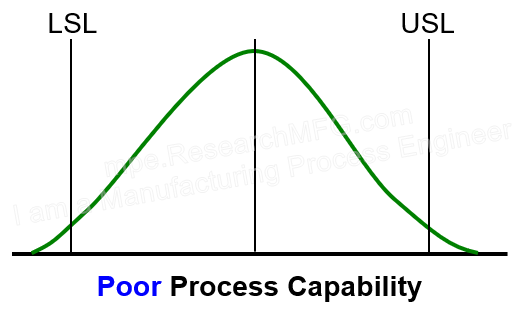
| ▼The center is also near the target, but the peak is too flat and the width goes beyond the spec limits. This means Ck is good, but Cp is poor. → About 10% of products are already outside the spec, and the results are scattered. This indicates very poor process capability, possibly due to loose machine mechanisms or nonconforming materials. The line should be stopped for equipment maintenance and to find the source of variation. |
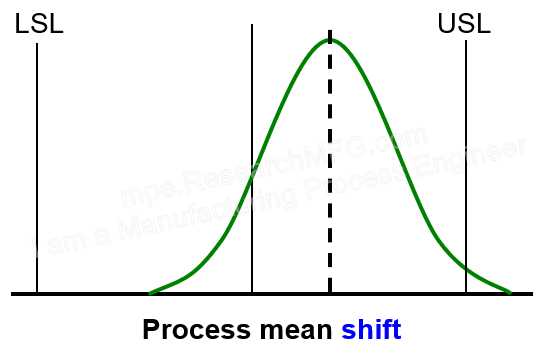
▼The center is slightly off from the target. The width is a bit smaller than the spec range, but part of the curve still goes outside the limits. This means Ck is not good, but Cp is barely acceptable. → This means the process is off-center. Some products are out of spec, but moving the process center back to the middle can quickly improve it to an acceptable level. |
|
 |
 |
How to Improve Process Capability
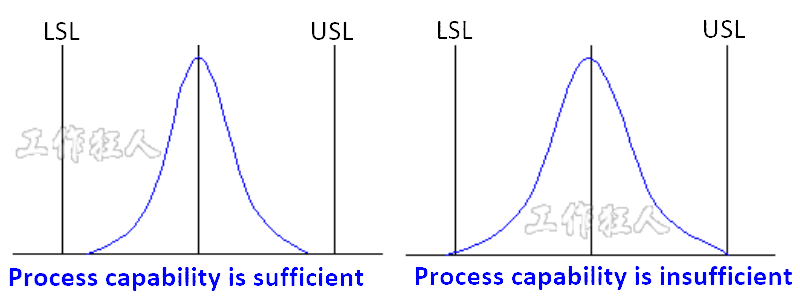
Looking at the normal distribution chart below, the original process capability is insufficient, with a certain percentage of products falling below the lower spec limit. There are two main countermeasures:
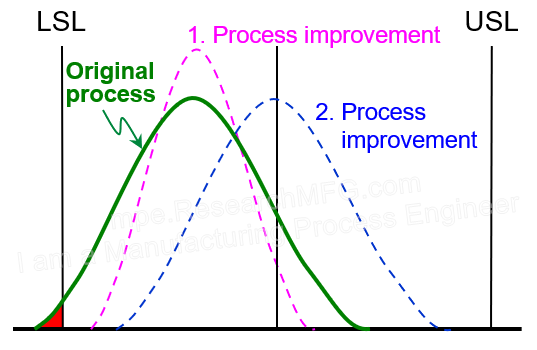
- Reduce process variation – Improve Cp by making the process more precise.
-
Shift the process center – Improve Ck or Ca by bringing the center closer to the spec center.
From a technical point of view, reducing process variation (improving Cp) often means buying new machines to reduce dimensional errors, or demanding more precise part dimensions. On the other hand, shifting the process center is usually simpler—this can often be done by adjusting machine settings, modifying assembly methods, or controlling key dimensions with control charts.
In short, shifting the process center is usually easier than reducing process variation. Most people will try this method first to quickly improve yield.
》Overview and Explanation of SPC, Cpk, and Process Capability
Related Posts:
About Statistical Process Control (SPC):




Leave a Reply