Understanding Cp as a Process Capability Indicator
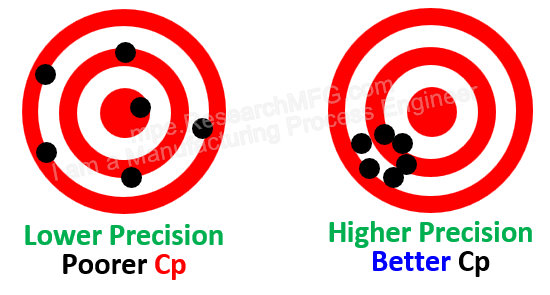
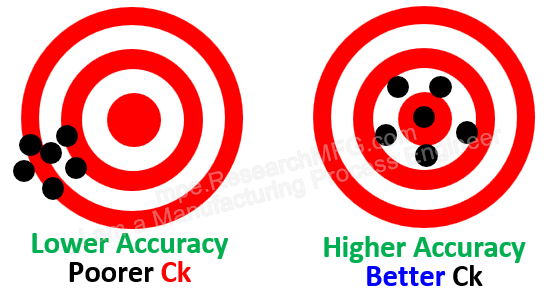
Cp (short for Precision) is a measure of how tightly a process is centered and how consistently it produces results. Using a target-shooting analogy, if someone fires six bullets and they all hit the same tight spot, that means the process has high Cp. The tighter the grouping, the higher the Cp value.
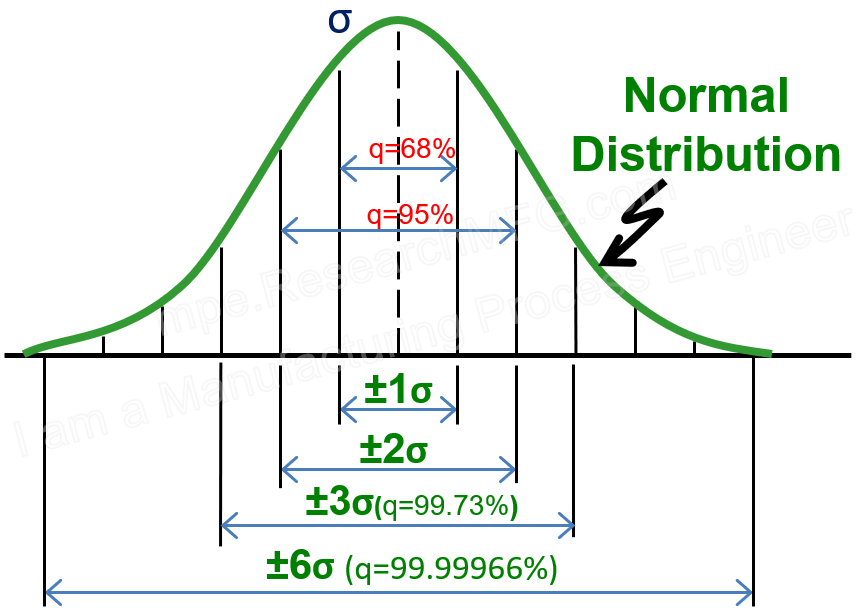
From the perspective of a normal distribution, about 99.73% of the population falls within ±3σ (standard deviations). In other words, a range of 6σ roughly represents the full spread of the data. However, this still allows for a potential defect rate of 0.27%, or 2700 parts per million (ppm).
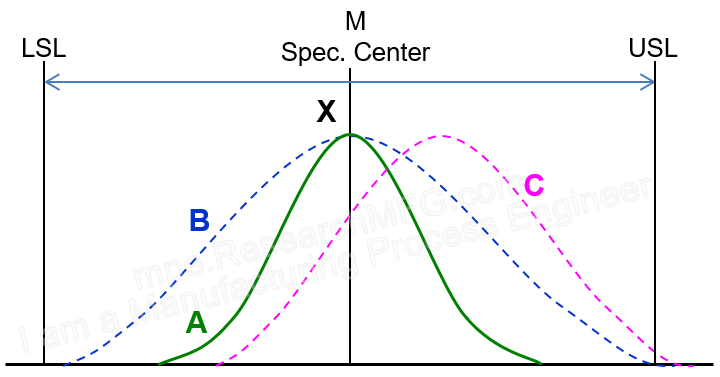
In general, Cp is used to evaluate how “wide” or “narrow” the process variation is. A wider spread means poorer capability, while a narrower spread means better capability. But how narrow is good enough? And how wide is too wide? That’s why we compare the 6σ spread to the specification width (T). This ratio is the heart of what Cp is about.
Cp Formula
| Cp=T/(6σp) | Where T is the specification width, and σp is the standard deviation of the process. The higher the Cp, the better. |
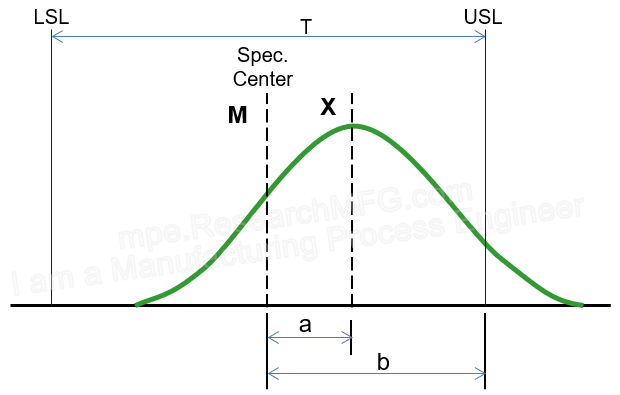
| (1) When there are two-sided specifications: | Cp=T/(6σp), T = USL – LSL USL = Upper Specification Limit LSL = Lower Specification Limit |
| (2) When there is only an upper limit: | Cp=(USL-X)/(3σp), X = Process mean; If X > USL, Cp = 0 Some characteristics, like flatness, roundness, or concentricity, are one-sided specifications with a lower limit of 0. In these cases: Cp=(USL-0)/(6σp) |
| (3) When there is only a lower limit: | Cp=(X-LSL)/(3σp) If X < LSL, Cp = 0 |
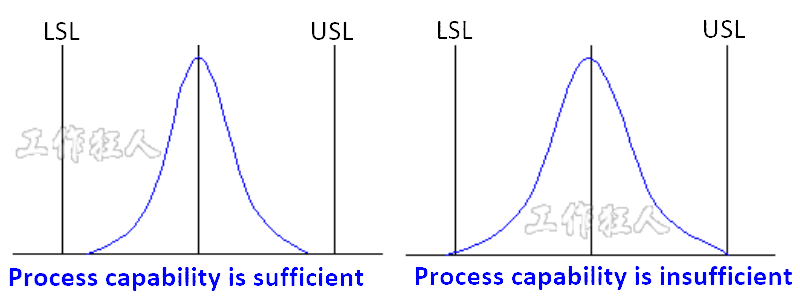
How to interpret Cp levels
| Grade | Cp Range | Explanation | |||||
|
A |
1.33 |
≦ |
Cp |
|
Process is stable. May consider relaxing specifications or sampling less. | ||
|
B |
1.00 |
≦ |
Cp |
< |
1.33 |
Currently okay, but close to limits. Monitor for shifts in the process. | |
|
C |
0.83 |
≦ |
Cp |
< |
1.00 |
Process capability is insufficient. Improvements should be made. | |
|
|
|
|
Cp |
< |
0.83 |
Major issues. Review all factors; may need to stop production if necessary. | |
》Overview and Explanation of SPC, Cpk, and Process Capability
Related Posts:




Leave a Reply